Magnetic Nanodiscs Enable Remote Magnetomechanical Neural Stimulation
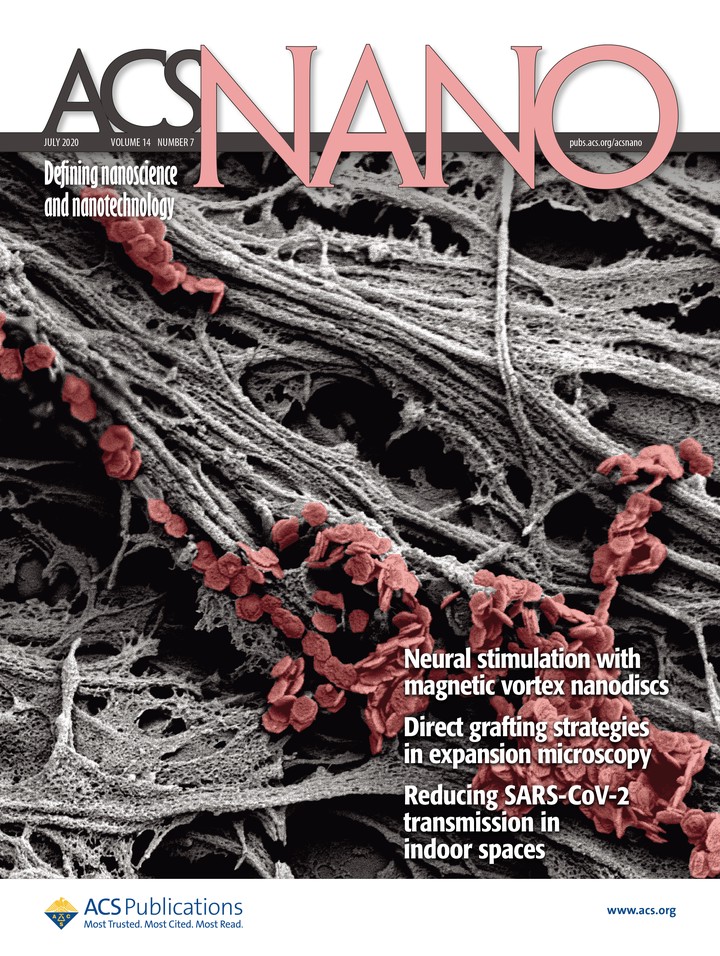 Magnetite nanodiscs decorating axons extending from a sensory neuronal structure dorsal root ganglion in vitro revealed by scanning electron microscopy. Switching from the vortex to in-plane magnetization state enabled the nanodiscs to transduce torques to the membranes of mechanosensitive neurons and, thus, to trigger their activity via remotely applied magnetic fields.
Magnetite nanodiscs decorating axons extending from a sensory neuronal structure dorsal root ganglion in vitro revealed by scanning electron microscopy. Switching from the vortex to in-plane magnetization state enabled the nanodiscs to transduce torques to the membranes of mechanosensitive neurons and, thus, to trigger their activity via remotely applied magnetic fields.